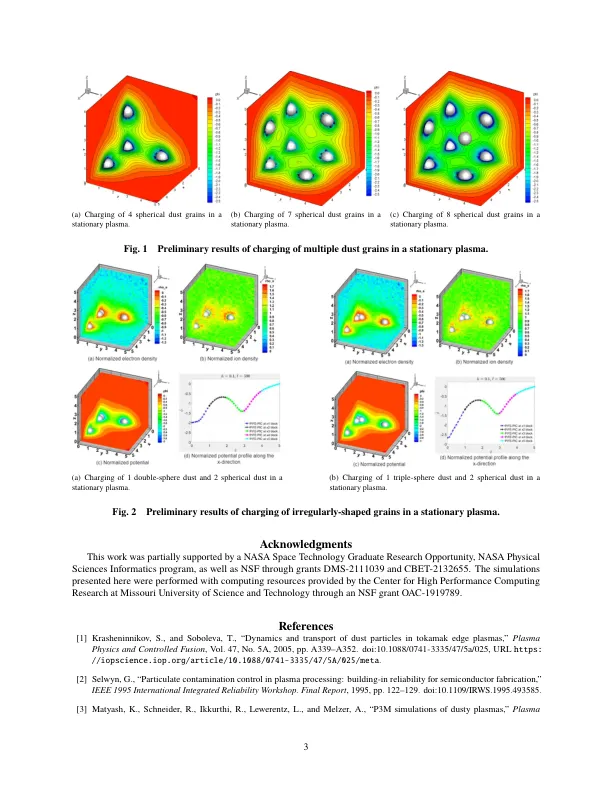
II. Introduction P lasmas that contain solid particulates (grains) much more massive than the ions present are usually referred to as “dusty plasmas” and are encountered in many fusion/laboratory and industrial plasmas and combustion processes, as well as in the space environment [ 1 , 2 ]. The electrodynamical interactions among dust grains and plasmas can strongly influence the behavior of plasma devices such as tokamak and industrial combustion reactors. Previous efforts have been put into both microscopic dust charging and macroscopic dust transport scales. For instance, at the microscopic (grain) scale, particle-particle, particle-mesh (P3M) approach has been used to study charging process of micro-meter sized grains in low temperature plasmas [ 3 ]. The Particle-in-Cell (PIC) - Monte Carlo Collision (MCC) approach was used for plasma particles while the PIC - Molecular Dynamics (MD) approach was used for Coulomb interactions among the dust grains. Results show that the amount of charge on the dust grain Q d could be on the order of Q d / e ∼ 3000-7000 negative ( e is the elementary charge) within the sheath. Other grain-scale charging models include a “patched charge model” using the capacitance of an isolated spherical dust grain and empirical constants based on experiment data, predicting the Q d on the order of Q d / e ∼ 10 4 [ 4 ], and a test-particle approach supercharging model using a boundary-element-based surface charging method with a multipole electric field solver, predicting the Q d on the order of Q d / e ∼ 10 2 [ 5 ] under similar plasma conditions to the patched charge model. The stochastic charging nature at the grain scale also leads to charge fluctuations [ 6 ], heating [ 7 ], and oscillations [ 8 – 10 ]. At the macroscopic (device/system) scale, electrodynamical
Charging of Irregularly-Shaped Dust Grains near Surfaces in Space