机构名称:
¥ 1.0
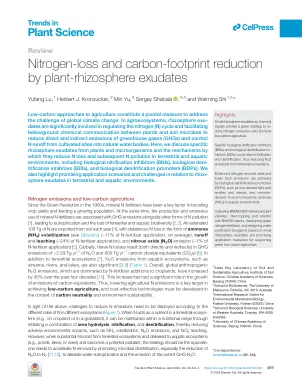
低碳方法的农业构成了应对全球气候变化挑战的关键措施。在农业生态系统中,根际的显着参与调节氮(N)循环,并促进植物与土壤微生物之间的地下化学通信,以减少温室气体(GHGS)的直接和间接排放,并从耕种地点进入自然水体。Here, we discuss speci fi c rhizosphere exudates from plants and microorganisms and the mechanisms by which they reduce N loss and subsequent N pollution in terrestrial and aquatic environments, including biological nitri fi cation inhibitors (BNIs), biological deni- tri fi cation inhibitors (BDIs), and biological denitri fi cation promoters (BDPs).我们还强调了与根部和水生环境中的根茎相关的有希望的应用程序和挑战。
通过植物 -
主要关键词