XiaoMi-AI文件搜索系统
World File Search System调动资本扩大巴西农作物和牲畜的负责任扩张
更好地利用现有土地:与普遍认为的产量增加会加大对自然生态系统的压力相反,巴西和其他地区的实证研究表明情况恰恰相反。为了减少对环境的影响,一种策略是提高现有农田的粮食产量,尽量减少对额外农田的需求,并保留土地用于栖息地保护。在巴西,1960-2000 年间农业现代化带来的生产力增长减缓了森林砍伐,因为农民转向了资本与土地比率更高的做法,有助于保护自然资源。更好地利用土地还意味着应根据每个地区的社会环境特点调整做法。对生物多样性、水资源的影响、该地区的社会影响和当地社区的生计等因素应成为深入分析的对象。
植物和牲畜组织DNA纯化的Sbeadex闪电协议
7。将磁铁与管接触,直到所有Sbeadex颗粒形成一个沉淀(通常取决于样品类型)。在继续步骤8之前,请确保将所有Sbeadex颗粒均匀。8。卸下上清液并丢弃。确保去除尽可能多的上清液,并注意不要脱离颗粒。9。将适当的洗脱缓冲液放大器和涡流添加60秒。或者,涡旋30秒,在60°C下孵育1-5分钟。洗脱缓冲液AMP体积应为步骤1中使用的裂解物体积(例如如果使用了200 µL裂解液,请添加100 µL洗脱缓冲液AMP)。为了获得较高的浓缩DNA,可以将洗脱缓冲液体积减小到20 µL。
1 5K牲畜和散装Pty Ltd Ravensthorpe WA 6346 ...
损失我的40%的业务将大大减少,可能会消除我在设备上偿还债务的能力。由于这一决定及其对业务信心的影响,设备正在迅速折旧。现在非常不愿投资设备。闲置的设备将很快变得无法使用和毫无价值。如果我无法为债务提供债务,我的业务是不可行的。我将无法用当地工作替换现场绵羊出口留下的赤字,因为它根本不可用。可以可笑地建议,因为有一个卡车司机的短缺,我可以按照逐步的小组报告的建议开始在其他部门驾驶卡车。这一严重歪曲了我们是遭受一系列竞争力量的农村企业的事实,并承担着巨大的间接费用,在较小的利润率下,以4-5%的价格付出了。我的业务通过使用机械师,轮胎商店,当地购物以及光顾其他当地企业等本地服务为我们的当地做出了巨大贡献。我目前赞助了两个已经努力支持的足球队和其他几个社区团体。此赞助将不再可用。
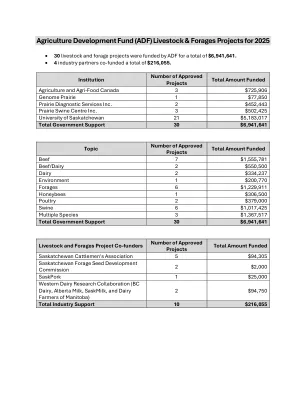
农业发展基金(ADF)牲畜和饲料项目2025
•相对于放牧系统(连续与旋转放牧系统),在放牧期间量化了牛和小牛的生长,以及放牧季节结束时的繁殖率。•测量牛的肠甲烷相对于放牧系统的产生。•表征牛的粪便微生物组,并将其与肠ch4产量相关联并建立肠ch 4的生物标志物。•增强肠甲烷对遗传潜力的基因组预测,以在放牧时选择减少排放的牛。•将牛水平的数据与土壤,植被,温室气体排放和社会经济结果相结合。ADF资金:$ 314,801苜蓿中的气候变化弹性,以增强牛肉和乳制品生产的盈利能力和可持续性。(20240701)首席研究员:Stacy Singer,农业和加拿大农业食品
基因编辑技术的改进提高了其在牲畜中的应用
基于新型CRISPR/CAS9基因组编辑技术的加速开发提供了一种可行的方法,可以在哺乳动物基因组中引入各种精确的修饰,包括同时引入多个编辑,并有效地将长DNA序列的插入插入到特定的目标位置以及执行核核的特定位置。因此,CRISPR/CAS9工具已成为引入牲畜基因组改变的首选方法。新的基于CRISPR/CAS9的基因组编辑工具的列表正在不断扩展。在这里,我们讨论了为提高基因编辑工具的效率和特殊性的方法,以及可用于基因调节,基础编辑和表观遗传修饰的方法。此外,将讨论两种用于生产基因编辑农场动物的主要方法的优势和缺点:将讨论体细胞核转移(SCNT或克隆)和合子操作。此外,我们将回顾基因编辑技术的农业和生物医学应用。
牲畜基因组的结构变异及其与表型特征的关联:综述
基因组结构变异(SV)是指基因组尺度上个体间基因序列的差异,其在基因组中分布广泛,主要表现为插入、缺失、重复、倒位和易位等。SV具有片段长、覆盖范围大的特点,对家畜遗传特性和生产性能有显著影响,在研究品种多样性、生物进化、疾病相关性等过程中发挥着重要作用。对SV的研究有助于加深对染色体功能和遗传特性的认识,对理解遗传性疾病的发生机制具有重要意义。本文对牛、水牛、马、绵羊和山羊基因组中SV的概念、分类、主要形成机制、检测方法及研究进展进行综述,旨在通过基因组研究揭示表型性状差异的遗传基础和适应性遗传机制,为更好地认识和利用草食家畜遗传资源提供理论基础。
牲畜实验室-Steen OOI,博士Andrew Sayles -Bubble
牲畜实验室(LL)将使用先进的基因工程,数据分析和机器学习技术来创建出色的优质细胞系。ll将提供经过验证的细胞系集合,这些细胞系被证明可以扩展,完全脱离风险,并提供一流的单元线工程(控制,稳定性等)。即使是不喜欢GM的公司(不到所有报告的公司的一半)也需要GM细胞在其研发过程中,因为GM细胞稳定,并且可以在实验中提供可靠的常数。
政策简报 印度尼西亚牲畜使用过期口蹄疫疫苗
3) 在广泛使用之前,应在牛身上对各批次疫苗进行独立测试,以检测其是否产生 FMDV 抗体,具体如下:• 应使用每批次的样品对一组 5 头无 FMDV 测试牛(与其余牛群隔离)进行接种。这需要在整个过程中保持极高的生物安全性。• 应通过病毒中和试验 (VNT) 和非结构蛋白 (NSP) ELISA 测量接种后第 0 天和第 21 天收集的血清中诱导的 FMDV 抗体水平。• 应将第 0 天和第 21 天的血清送至有资质的 FMD 参考实验室进行检测。这将提供过期疫苗抗原含量的血清学读数,并给出预期保护的指示。
新基因组学技术——改良农作物和牲畜的多功能工具箱
史蒂文·鲁诺 (Steven Runo) 是肯尼亚内罗毕肯雅塔大学的分子生物学教授。他从肯雅塔大学获得了理学学士和理学硕士学位。随后,他获得洛克菲勒基金会的博士奖学金,作为肯雅塔大学和加州大学戴维斯分校合作项目的一部分,研究分子生物学。 2008年获得博士学位后,他在谢菲尔德大学(英国)和弗吉尼亚大学(美国)完成了博士后项目,之后返回肯尼亚并在肯雅塔大学担任讲师。目前,他的实验室正在利用分子遗传原理了解限制非洲农业生产的寄生植物及其与宿主的相互作用。史蒂文是亚历山大·冯·洪堡研究奖学金和乔治·福斯特高级研究奖学金的获得者。为了表彰他对科学的贡献,史蒂文·鲁诺于 2020 年被授予皇家学会非洲奖。 https://spas.ku.ac.ke/department-of-biochemistry-faculty/prof-steven-runo
社论:基因组学在选择或保护牲畜种群中的应用
Genomics is one of the newest branches of biology that has progressed tremendously during the last decades. Genomics deals with the molecular structures, functions, evolution, and mapping of the genomes of any species and has signi fi cantly generated new information that has improved our understanding of the complex biology and genetic mechanisms of animal production systems. The advancement of genomics is linked with a number of key developments, which include the rapid expansion of next-generation sequencing and chip- based genotyping assays. Large-scale genomics data are now utilized more and more due to the dwindling cost of such sequencing and genotyping techniques. Livestock breeding programs, including selection and conservation efforts, have attained huge success due to affordable genomic prediction, particularly in dairy cattle. It is expected that there will be further reduction in the cost of these high-throughput genomic data generation platforms and more development of precise estimation methodologies. Multi-disciplinary involvement is going to further bene fi t the genomics community with the advancement of robust and reliable tools in the fi eld of bioinformatics and their use in livestock breeding. Keeping these developments in the area of livestock genomics in mind, the present Research topic of the Frontiers in Genetics titled “ Application of Genomics in Livestock Populations under Selection or Conservation ” was aptly selected with several major themes that highlighted the usage of genomics for conservation, current methods of genomics, application of whole-genome- and genome-wide-based techniques, and use of different bioinformatics tools and pipelines for the processing of genomic data. The resulting efforts contributed to the publication of a total 19 research papers in the current volume, comprising major focal points in the area of genomics of livestock and other species with the concerns of the present day. However, the ocean of genomics is too vast, and even this wide-array of published articles could hardly justify an ounce of that vastness! Nonetheless, genuine efforts were made to include articles in this volume on those central themes of genomics that comprise the major skills and techniques employed in various animal populations for selection and conservation issues. These include genome- wide association studies (GWAS), differential gene expression utilizing transcriptome data, and analysis of selection signatures through whole-genome sequencing and high-density genotyping datasets, which are utilized for discovering genes and genomic variants that control signi fi cant traits of importance in livestock species.