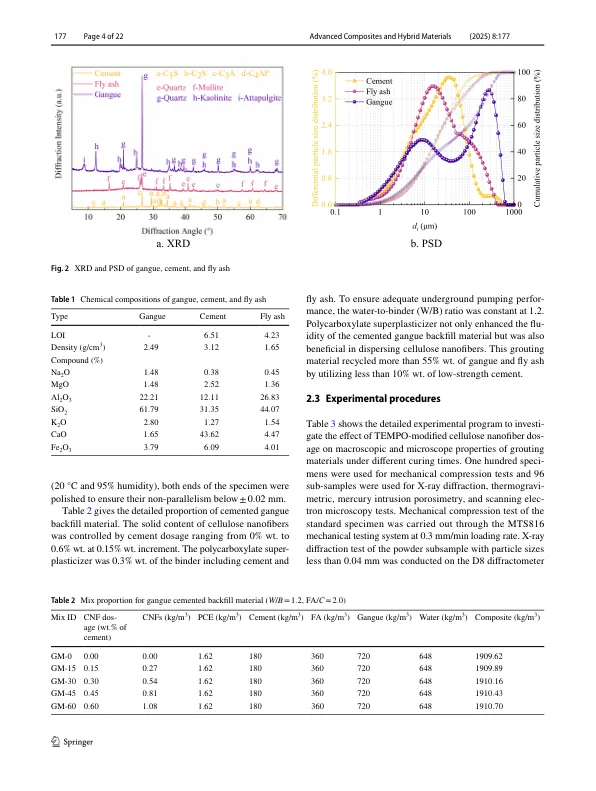
摘要加强胶结回填材料以回收脉管和尾矿的性能对于矿产资源和采矿废物管理的可持续发展至关重要。然而,在低成本,高废物比,低碳排放和低粘合剂消耗的实际限制下,巩固了毒性,毛孔和对具有卓越特性的水泥回填材料的采矿废物的升级,这是固有的矛盾和挑战性的。这项研究报告了一种废物到富裕途径,该途径通过纤维素纳米纤维来改善胶结的螺栓回填材料,以回收采矿废物并部分取代水泥。Mechanical compression, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry, mercury intrusion porosimetry, scanning electron microscopy tests, fractal quantitative analyses of microstructures, and molecular dynamics simulations were carried out to reveal the action mechanism of TEMPO-modified cellulose nanofibers on cemented gangue backfill materials.分析了节气改性纤维素纳米纤维和机械纤维素纳米纤维对胶结螺栓回填材料强度的贡献的差异。The results show a series of microscopic improvements of cellulose nanofibers on cemented gangue backfill materials, including regulating cemented gel polymerization, increasing hydration nucleation, inhibiting carbonization, densifying pore structure, enhanc- ing Ca-O connections and H bonds, and preventing C-S–H fracture along interlayer water.通过纤维素纳米纤维诱导的这种胶结材料的强度和能量吸收增强,具有最佳剂量可达到30〜50%。还发现过多的纤维素纳米纤维对这种复合材料有害,主要是通过延迟水合结晶并通过捕获空气增加孔,而尽管强度恶化,但它仍然表现出改善的变形抗性和能量吸收。
纤维素纳米纤维的微观机制修饰的胶结脉冲回填材料
主要关键词