机构名称:
¥ 1.0
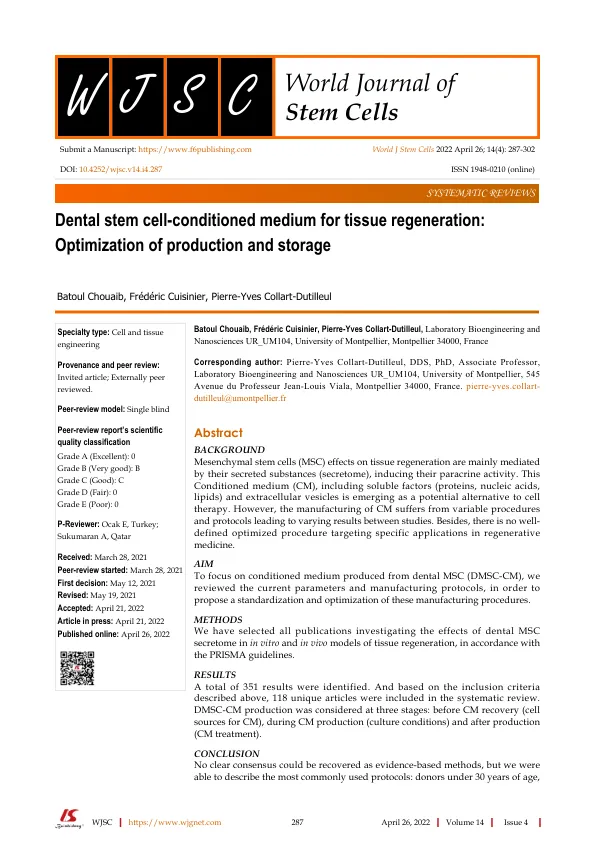
尽管间充质干细胞(MSC)最初是从骨髓中分离出来的,但牙科和牙周组织(DMSC)的MSC由于其实际和技术优势而引起了未来疗法的国际关注[1]。Since 2000, when Gronthos et al [ 2 ] described a population of pluripotent progenitors in adult dental pulp, studies have shown that dental tissues can be an important resource of MSCs: dental pulp stem cells (DPSC), exfoliated deciduous tooth stem cells (SHED), apical papilla stem cells (SCAP) which are situated at the ends of growing dental roots[ 3 ], periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSC),位于牙齿胚芽周围的牙齿卵泡干细胞(DFPC),并在牙齿发育过程中负责牙骨质,牙周韧带和肺泡骨形成[4],牙龈衍生的间充质干细胞(GMSC)(GMSC)(图1)。在发育早期(贝尔阶段)的牙齿中,已经描述了来自牙齿间充质的多能祖细胞,称为牙齿胚芽祖细胞(TGPC)[5]。
组织再生的牙科干细胞条件培养基