机构名称:
¥ 1.0
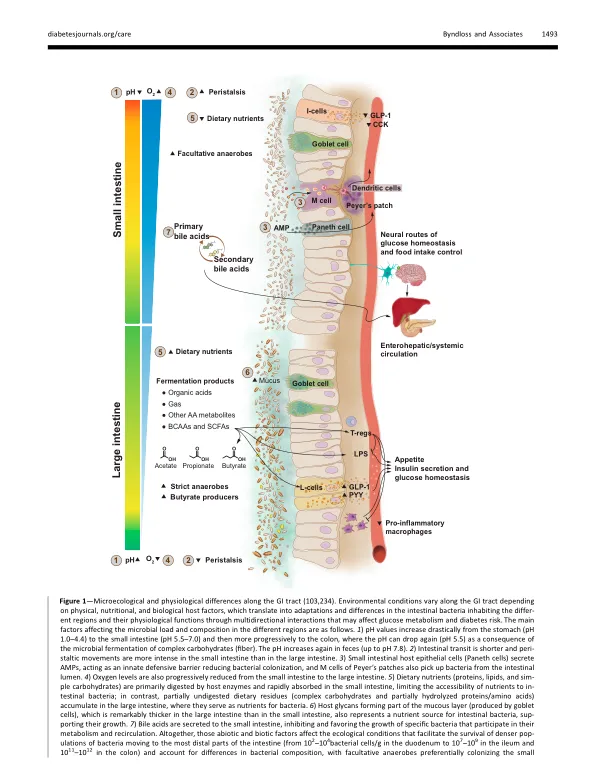
本文总结了肠道菌群(GM)在糖尿病,糖尿病,糖尿病护理和糖尿病学组织的糖尿病中的作用的科学状态,该论坛在欧洲糖尿病研究协会举行,该协会在德国汉堡在汉堡举行的糖尿病研究协会。论坛包括临床医生和基础科学家,他们是肠道微生物组和新陈代谢领域的领先研究人员。Their conclusions were as fol- lows: 1 ) the GM may be involved in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes, as microbially produced metabolites associate both positively and negatively with the disease, and mechanistic links of GM functions (e.g., genes for butyrate pro- duction) with glucose metabolism have recently emerged through the use of Mendelian randomization in humans; 2)GM的高度个性化的性质构成了重大的研究障碍,并且对关联和因果关系进行了强有力的评估,需要大量的人群和深层的核基因组方法; 3)因为单个 - 时间点抽样错过了个体内部的GM Dynamics,因此需要在个体内进行重复测量的未来研究; 4)将需要许多未来的研究来确定这种不断扩展的知识对糖尿病诊断和治疗的适用性,而新颖的技术和改进的计算工具对于实现这一目标至关重要。
肠道菌群和糖尿病
主要关键词