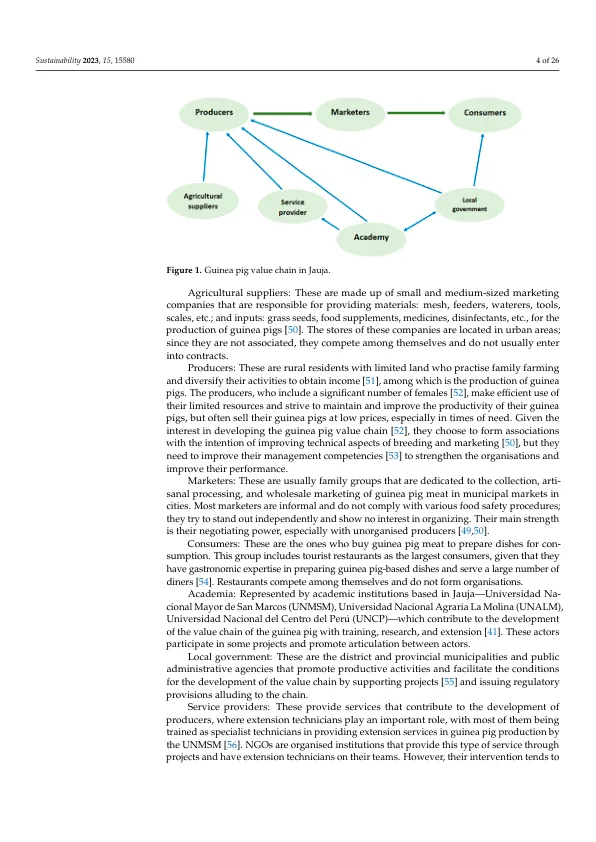
摘要:秘鲁Jauja的豚鼠价值链是通过应用生产项目,机构加强和实施负责农业和食品系统(CFS-RAI)的原则来开发的。鉴于Jauja领土的小小的条件和商业豚鼠育种的扩散,该链中的参与者构成了发展的关键人力资本。To improve the performance of the actors in the sustainable rural development of the territory of Jauja, Peru, the research carried out an evaluation of the competencies and capabilities for project management in 46 actors linked to the business programme on the CFS-RAI Principles, representing 1094 people in the guinea pig value chain in Jauja, using the Working With People (WWP) model and empirical instruments based on the Octagon method,项目管理能力评估,专家进行的绩效评估,态度评估。和商业模型画布。结果有助于构建价值链的参与者,他们表现出了对项目管理能力(2.73/5)的中间掌握,发展中的机构能力(2.89/7)以及不断增长的组织管理绩效(26.2/100)。此外,链中的参与者之间已经产生了信任和积极性,并有兴趣继续实施CFS-RAI原则,以便在其商业创新的生产项目中实现可持续性。结果使我们能够为能力开发的创新计划设计,该计划与国际项目管理协会(IPMA)定义,在与CFS-RAI原则有关的情况下,平衡了项目管理能力(观点,人员和实践)的三个维度。这两个过程都通过可持续项目管理和为该地区的可持续发展做出贡献,补充了农业资本链中人力资本的加强。
可持续性-Archivo Digital UPM
主要关键词