机构名称:
¥ 1.0
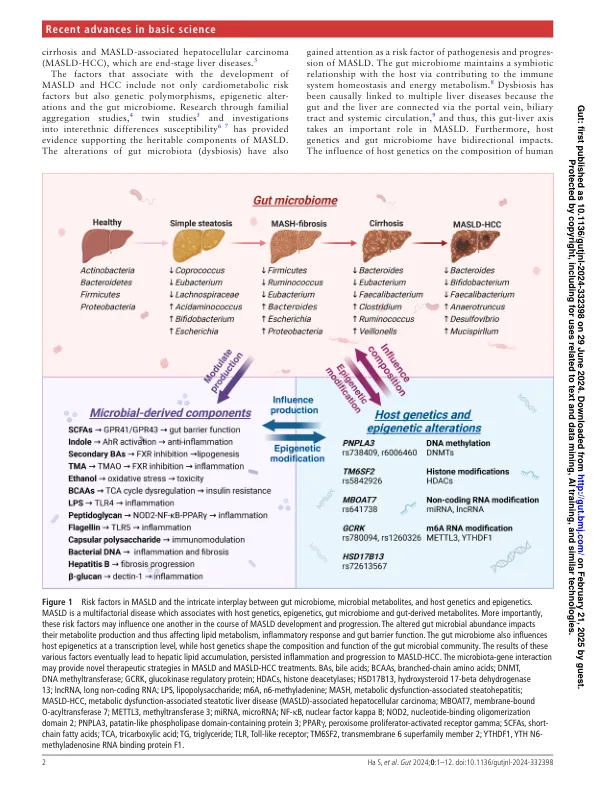
ABSTRACT Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) encompasses a wide spectrum of liver injuries, ranging from hepatic steatosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis to MASLD-associated hepatocellular carcinoma (MASLD-HCC).最近的研究强调了宿主遗传学/表观遗传学与肠道微生物群落之间的双向影响。宿主遗传学会影响肠道微生物组的组成,而肠道微生物群及其衍生的代谢产物可以诱导宿主表观遗传修饰,以影响MASLD的发展。探索肠道微生物组与宿主的遗传/表观遗传组成之间的复杂关系将产生针对MASLD及其相关条件的治疗干预措施的有希望的途径。在这篇综述中,我们总结了MASLD和MASLD-HCC中肠道微生物组,宿主遗传学和表观遗传学改变的影响。我们进一步讨论了研究发现,表明肠道微生物组和宿主遗传学/表观遗传学之间的双向影响,强调了这种相互联系在MASLD预防和治疗中的重要性。
相关的肝细胞癌
主要关键词