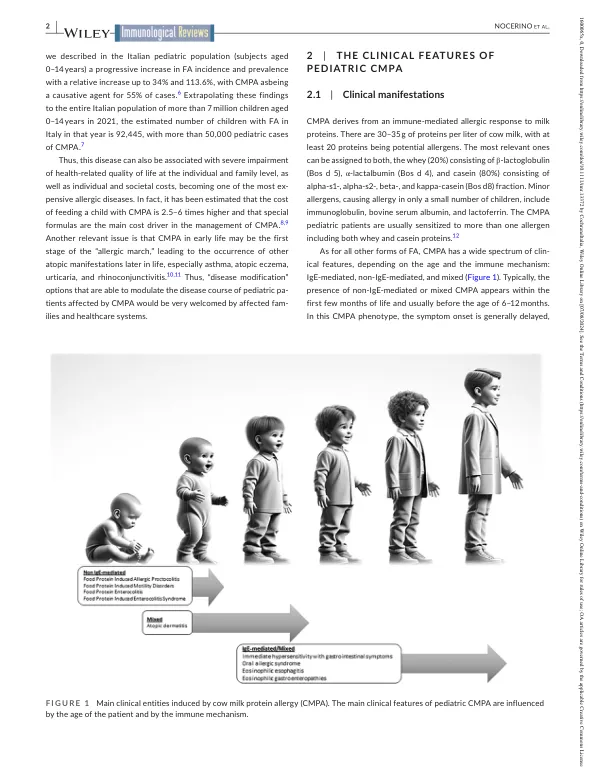
fi g u r e 2牛奶蛋白过敏(CMPA)金字塔。Children with CMPA have an elevated risk of developing other conditions within the allergic march (i.e., atopic dermatitis, urticaria, asthma, oculorhinitis, eosinophilic esophagitis [EoE]) or outside the allergic march such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), functional gastrointestinal disorders (FGIDs), and神经精神疾病。各种遗传因素在促进这些疾病的发生中起作用,但新兴的数据突出了肠道微生物组营养不良的关键作用,由环境因素引起。Emerging evidence supports the hypothesis that dysbiosis may be the initial trigger for alterations in the intestinal barrier and immune system function leading to CMPA and other allergic disorders later in life and the dysregulation of the brain-gut endocrine-immune system axis (leading to FGIDs, IBD, and neuropsychiatric disorders), partly through the activation of epigenetic mechanisms.
牛奶蛋白过敏的疾病修饰旅程
主要关键词