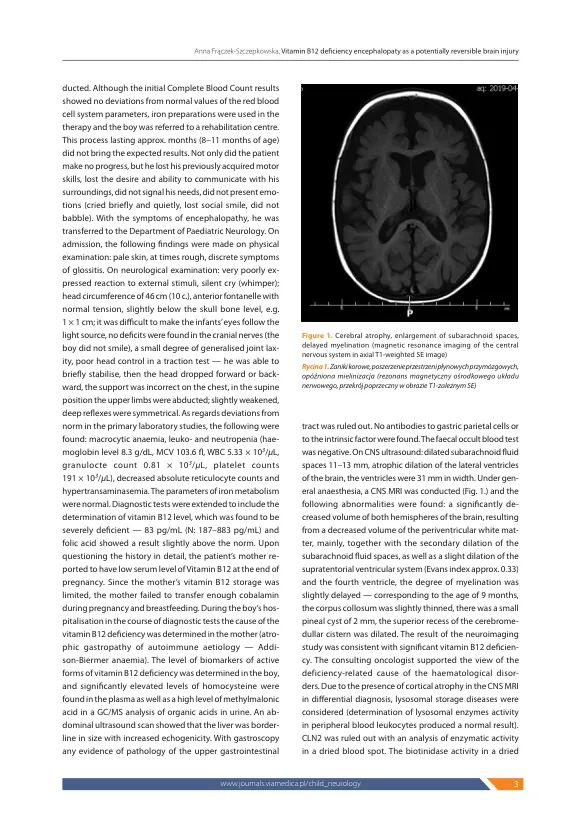
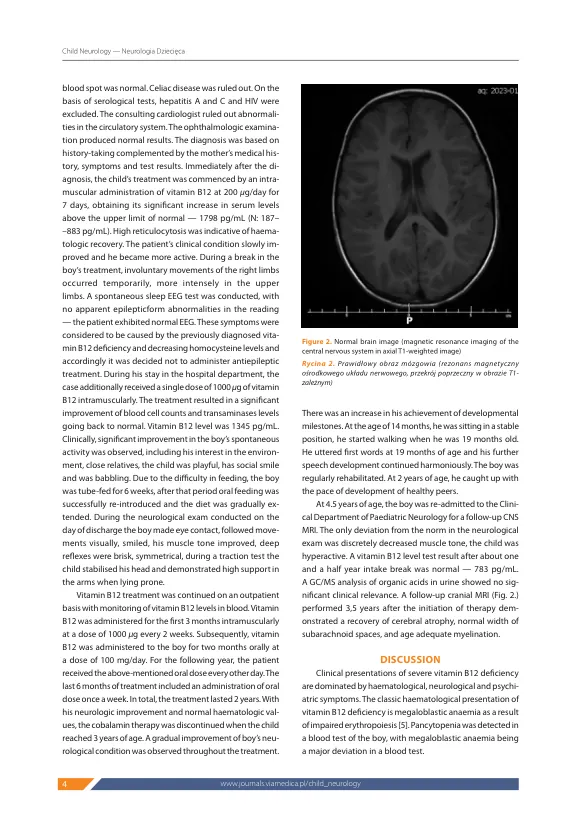
引言维生素B12,也称为钴胺素,是水溶性维生素之一。Cobalamin has a large variety of biological functions but above all it is essential for haemato poiesis and the development and functioning of the nervous system.它也会影响认知功能。维生素B12未在动物和植物生物中合成,细菌是其产生的原因。人类维生素B12的唯一来源是动物起源的食物[1]。表I中显示了针对单个组的建议每日摄入维生素B12的当前指南。The products richest in cobalamin are liver and kidneys (up to 100 µ g/100 g), but crustaceans, fish and meat also provide large amounts of cobalamin.鸡蛋,奶酪和牛奶含有相对较少的钴胺(6 µg/L)。维生素B12主要存储在肝脏中。从20%到90%的动物食品中,维生素B12的吸收不等。假定在胃功能正常的健康成年人中,这种维生素的约有50%是从饮食中吸收的。成人肝储存1-4毫克的成年肝储备平衡维生素B12脱落饮食几年[2]。相反,胎儿存储约。每天维生素的0.1–0.2 µg。 在生命的前六个星期中,在婴儿的血清钴胺素水平上看到了显着降低。 Moreover, infantile vitamin B12 body stores (which usually comprise about 25 µ g) may be much lower if the infant's mother is undernourished. 在Paedi雄性种群中,维生素B12缺乏症很少见。 本文每天维生素的0.1–0.2 µg。在生命的前六个星期中,在婴儿的血清钴胺素水平上看到了显着降低。Moreover, infantile vitamin B12 body stores (which usually comprise about 25 µ g) may be much lower if the infant's mother is undernourished.在Paedi雄性种群中,维生素B12缺乏症很少见。本文在钴胺素不足的原因中,饮食不足(饮食中的不足,饮食中的Min B12摄入量,素食饮食,素食饮食,营养不良,酒精中毒)主要突出显示,并且主要由胃肠道疾病和胃肠道疾病造成的吸收障碍,并由胃肠道疾病和遗传性疾病的替代性分发和植物性的vitemin BB12运输。胃原因包括城堡的内在因子缺乏,萎缩性胃病,Zollinger-Ellison综合征,质子泵抑制剂滥用,总或部分胃切除术。肠道原因包括腹腔疾病,克罗恩病,伊默隆德·格雷斯贝克综合征和寄生虫侵染(广泛的tape虫)[3]。它最常见的原因是食物不足,最脆弱的群体是由患有明显或潜在维生素B12缺乏症的母亲专门母乳喂养的婴儿[4]。
维生素B12缺乏症状作为潜在的...