机构名称:
¥ 1.0
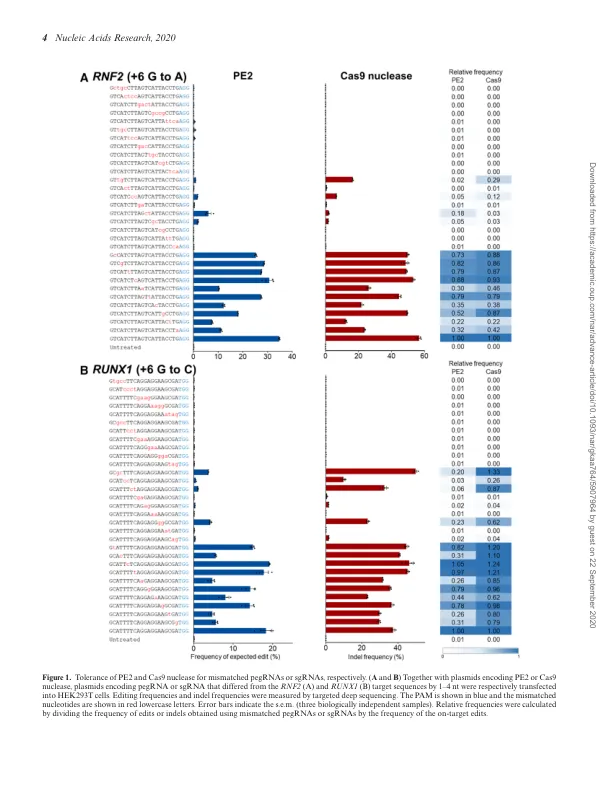
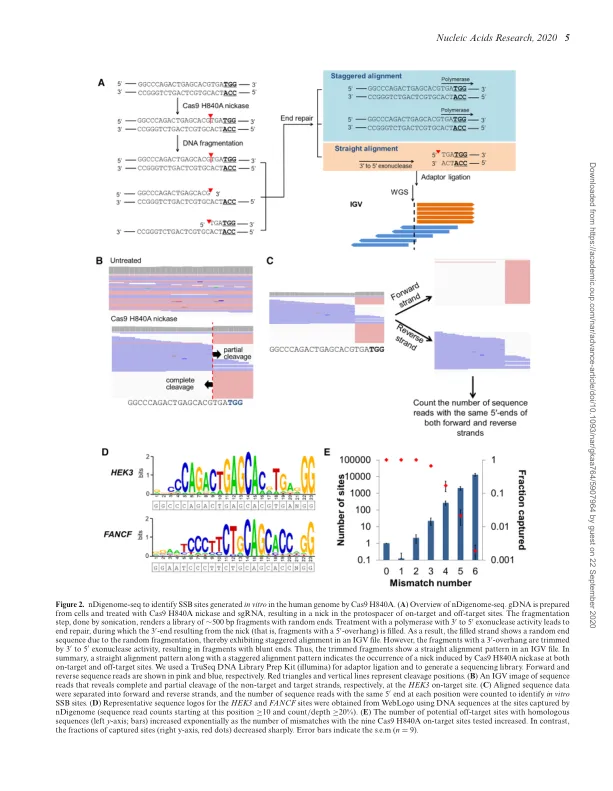
Prime编辑器(PES)可以在真核基因组中进行针对性的精确编辑,包括产生替代,插入和缺失。但是,尚未探索他们的全基因组规范。在这里,我们开发了基于Nickase的Digenome-Seq(Ndigenome-Seq),这是一种体外测定,它使用全基因组测序来识别由CRISPR诱导的单链断裂(群集经常间隔短的短质体重复序列)-CAS9(CAS9)(CAS9)(CRISPR与蛋白9)Nickase。我们使用ndigenome-seq筛选了潜在的基因组宽靶点位点Cas9 H840A Nickase(一种PE成分),该位点针对9个人类基因组部位。Then, using targeted amplicon sequencing of off- target candidates identified by nDigenome-seq, we showed that only five off-target sites showed de- tectable PE-induced modifications in cells, at fre- quencies ranging from 0.1 to 1.9%, suggesting that PEs provide a highly specific method of precise genome editing.我们还发现,通过工程化的Cas9变体(尤其是ESPCAS9和Sniper Cas9)将突变分解为PE,可以进一步改善人类细胞中的PE特异性。
与非... 相比 对主要编辑的特殊性的无偏见... 靶向衰老的治疗药物的进步 编辑创新的能源存储的高级高级材料:综合,表征和应用 使用基于群体的元疗法诊断心律不齐的诊断:比较分析 使用ECOC-SVM 的LSTM网络从静止状态EEG信号中分类非重生脑损伤
主要关键词