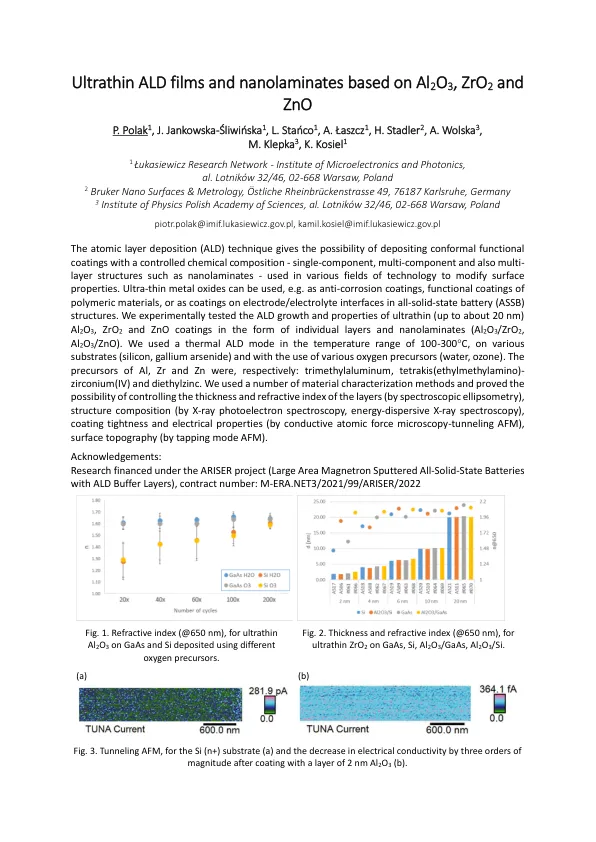
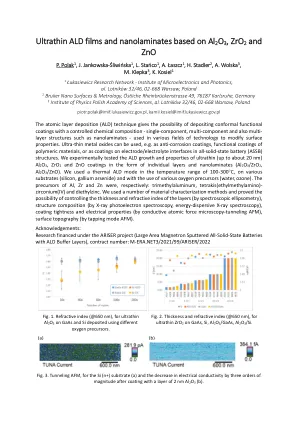
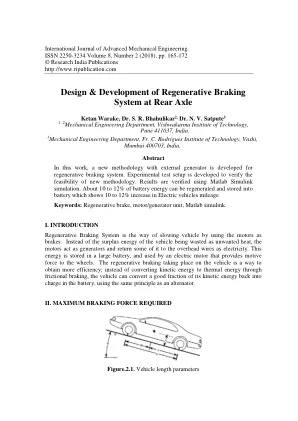
原子层沉积(ALD)技术使在各种技术领域中使用具有控制化学成分的共形功能涂层 - 单组分,多组分和多层结构(例如纳米胺),以修饰表面特性。可以使用超薄金属氧化物,例如作为抗腐蚀涂层,聚合物材料的功能涂层,或在全纤维状态电池(ASSB)结构中的电极/电解质界面上的涂层。我们以各个层和纳米酰胺的形式(Al 2 O 3 /Zro 2,Al 2 O 3 /ZnO)以实验测试了超薄(大约20 nm)Al 2 O 3,ZRO 2和ZnO涂层的ALD生长和性能。,我们在100-300 c的温度范围内使用了热ALD模式,在各种底物(硅,砷耐加仑)上以及使用各种氧气前体(水,臭氧)。Al,Zr和Zn的前体分别为:三甲基元素,四甲基甲基氨基(乙基甲基氨基) - 锆(IV)和二乙基。We used a number of material characterization methods and proved the possibility of controlling the thickness and refractive index of the layers (by spectroscopic ellipsometry), structure composition (by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy), coating tightness and electrical properties (by conductive atomic force microscopy-tunneling AFM), surface topography (by tapping mode AFM)。
基于Al2O3的超薄ALD膜和纳米胺,...
主要关键词