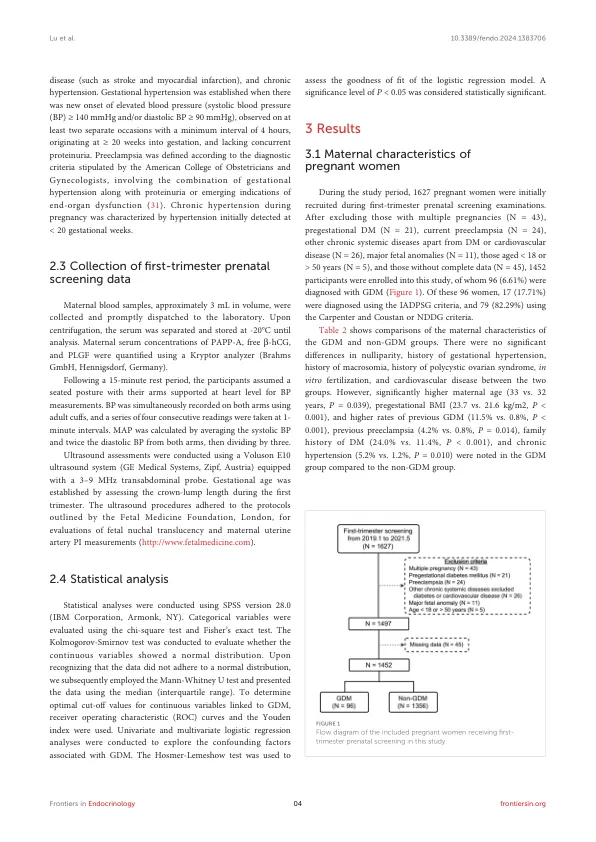
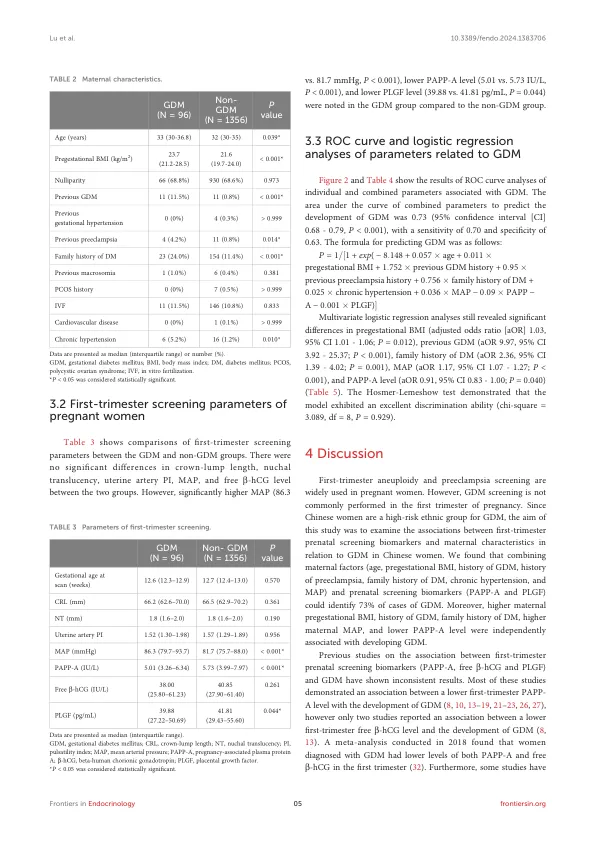
结果:在入学的1452名孕妇中,有96名发展GDM。PAPP-A(5.01 vs. 5.73 IU/L,P <0.001)和PLGF(39.88 vs. 41.81 pg/ml,p = 0.044)在GDM组中的明显低于非GDM组。联合母体特征和生物标志物的ROC曲线下的面积为0.73(95%的置置间隔[CI] 0.68 - 0.79,p <0.001)。The formula for predicting GDM was as follows: P = 1/[1 + exp (-8.148 + 0.057 x age + 0.011 x pregestational body mass index + 1.752 x previous GDM history + 0.95 x previous preeclampsia history + 0.756 x family history of diabetes + 0.025 x chronic hypertension + 0.036 x mean arterial pressure - 0.09 x PAPP -A -0.001 x PLGF)]。逻辑回归分析表明,较高的预性体重指数(调整后比值比[AOR] 1.03,95%CI 1.01-1.06-1.06,P = 0.012),以前的GDM历史记录(AOR 9.97,95%CI 3.92-25.92-25.37,P <0.001),p <0.001),diabetes的家族历史2.65%。 0.001),较高的平均动脉压(AOR 1.17,95%CI 1.07-1.27,p <0.001)和较低的PAPP -A水平(AOR 0.91,95%CI 0.83-1.00,P = 0.040)与GDM的发展独立相关。Hosmer-Lemeshow测试表明该模型具有出色的歧视能力(Chi-square = 3.089,df = 8,p = 0.929)。
头三个月筛查生物标志物之间的关联...
主要关键词