机构名称:
¥ 1.0
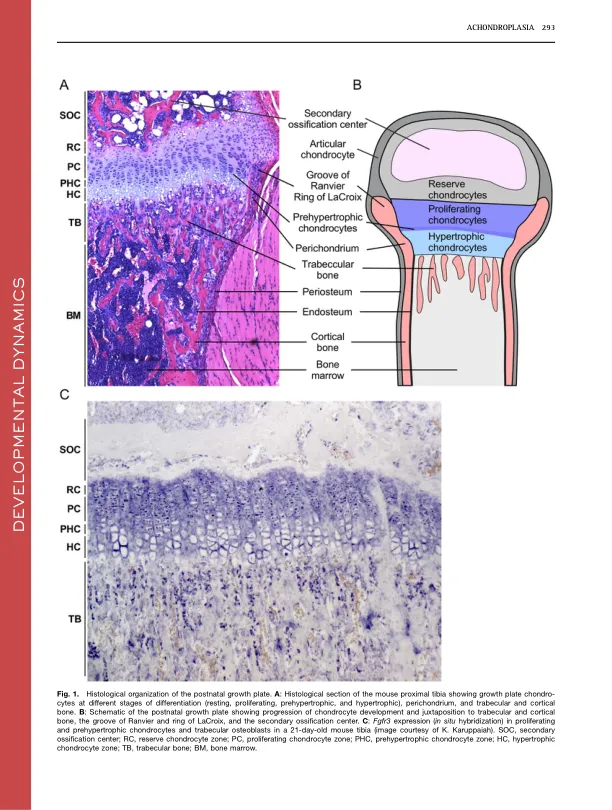
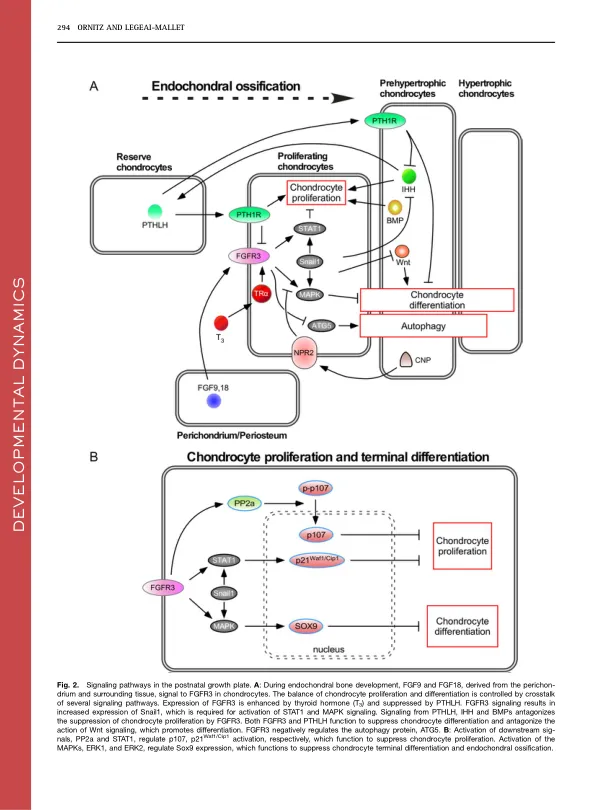
Autosomal dominant mutations in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 ( FGFR3 ) cause achondroplasia (Ach), the most common form of dwarfism in humans, and related chondrodysplasia syndromes that include hypochondroplasia (Hch), severe achon- droplasia with developmental delay and acanthosis nigricans (SADDAN), and thanatophoric发育不良(TD)。fgfr3在软骨细胞和成熟的成骨细胞中表达,其功能可调节骨骼生长。对FGFR3中突变的分析表明,通过包括稳定受体的机制,增强的二聚体和增强的酪氨酸激酶活性的结合,信号传导增加。矛盾的是,FGFR3信号的增加深刻抑制了生长板软骨细胞的增殖和成熟,导致生长板尺寸降低,小梁骨体积减少以及导致骨伸长降低。在这篇综述中,我们讨论了调节生长板的分子机制,即ACH的发病机理,ACH的发病机理以及正在评估的治疗方法,这些方法正在评估,以改善患有ACH和相关疾病的人的软骨骨生长。发展动力学246:291–309,2017。v C 2016 Wiley Wercenials,Inc。
adnondroploploplasia:发育,发病机理和治疗