机构名称:
¥ 1.0
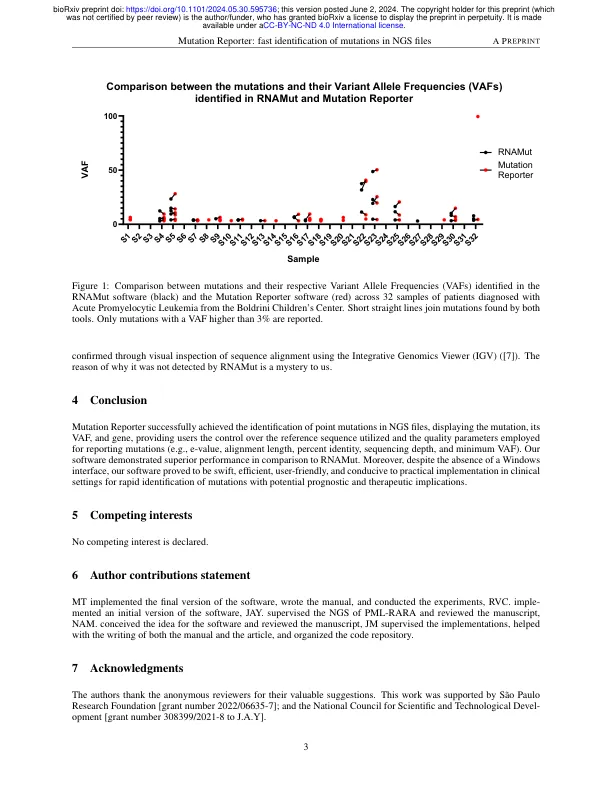
Next-generation sequencing (NGS) has emerged as a pivotal tool in precision medicine in oncology by enabling analysis of multiple genes at once and facilitating the detection of low-frequency mutations in patients, which may be implicated in treatment resistance, thereby underscoring the clinical significance of NGS in therapeutic decision- making ([5, 6]).然而,能够分析测序数据以识别突变的自由可用的开源软件工具的稀缺对生物学家构成了一个显着的挑战,而未经生物信息学培训。例如,最近描述的工具,即rNalut软件,迅速检测到突变并显示其频率,但缺乏功能,使用户可以理解和修改用于选择高质量读取的参数,或者指定最小的等位基因频率(VAF)以进行报告突变([4])。此外,缺乏有关用于比较的参考序列的披露是一个关键限制,尤其是对于随后对识别突变的功能研究。
长k-mers的简单有效采样算法
主要关键词