机构名称:
¥ 1.0
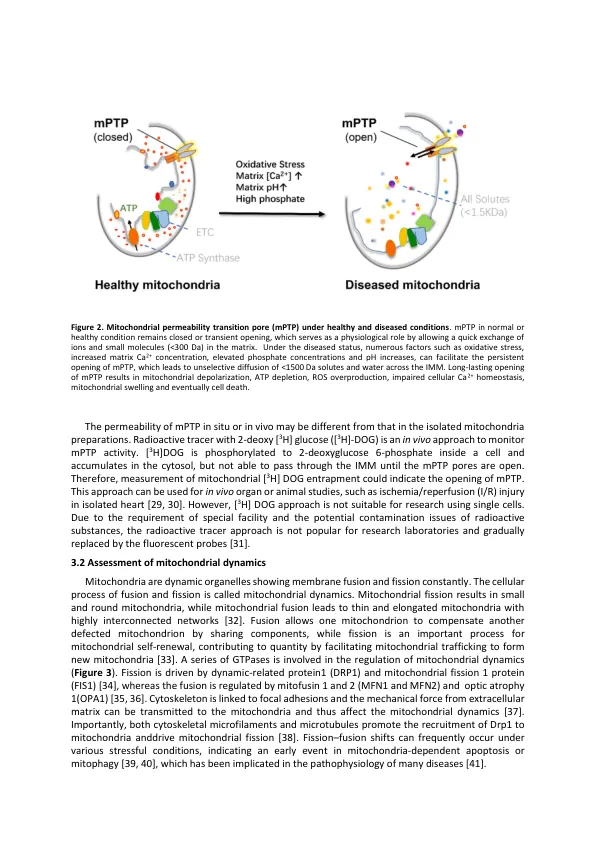
线粒体在细胞功能中起关键作用,不仅充当细胞的动力,而且还调节ATP合成,活性氧(ROS)产生(ROS),细胞内Ca 2+循环和凋亡。During the past decade, extensive progress has been made in the technology to assess mitochondrial functions and accumulating evidences have shown that mitochondrial dysfunction is a key pathophysiological mechanism for many diseases including cardiovascular disorders, such as ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, hypertension, atherosclerosis, and hemorrhagic shock.方法论的进步一直在加速我们对线粒体分子结构和功能,生物发生以及ROS和能量产生的理解,这促进了新的药物靶标识别和线粒体功能障碍疾病的治疗策略的开发。本综述将重点介绍当前用于线粒体研究的方法论,并讨论其优势,局限性以及线粒体功能障碍在心血管疾病中的影响。
通过葫芦对O-亚硝基苯酚进行荧光检测[8 ...